A domain name is the best way to improve the online identification of your website. It’s a unique address people use to find you online.
A subdomain is a subset of the main domain used to group and organize content within the same website. It is typically used to create separate sections or categories of a website.
If you search “Domain Vs Subdomain,” then might have heard about the Subdomain a few days ago and want to know what is this. So, don’t worry; we are here to give you a detailed explanation about Domain and Subdomain.
In this article, We’ll discuss Domain Vs Subdomain and compare their various features. So you’ll understand each use and choose according to your website’s requirements.
Quick Access
ToggleWhat is a Domain?
A domain name is the main address that people type in their browser to access your website. It consists of a top-level domain (TLD) and a domain name extension.
The TLD can be generic like .com, .net, or country-specific.UK, .fr. The domain name extension refers to the purpose or type of website it represents, like .org for organizations, .edu for educational institutions, etc.
For example, in www.example.com – “example” is the domain name, and “.com” is the TLD. Domains are purchased and registered through domain registrars, companies that manage the reservation of domain names.
The right domain name is crucial as it reflects your brand’s identity and is pivotal for establishing a solid online presence. It serves as a technical shortcut and a significant element of your brand’s marketing and searchability.
What is a Subdomain?
A subdomain is a prefix added to your original domain name, creating an additional, separate web address. It helps in organizing and navigating to different sections of your site.
For instance, blog.example.com is a subdomain where ‘blog’ is the subdomain prefix to the main domain ‘example.com.’ This structure helps separate distinct content areas, such as a blog or a store.
Subdomains operate independently of the main domain, offering the flexibility to host different content and applications. They can be created and managed with ease via your web hosting control panel.
Moreover, they are cost-effective, as multiple subdomains can be added without extra domain registration fees. This makes subdomains particularly favorable for smaller businesses or distinct projects.
Understanding URL Structure
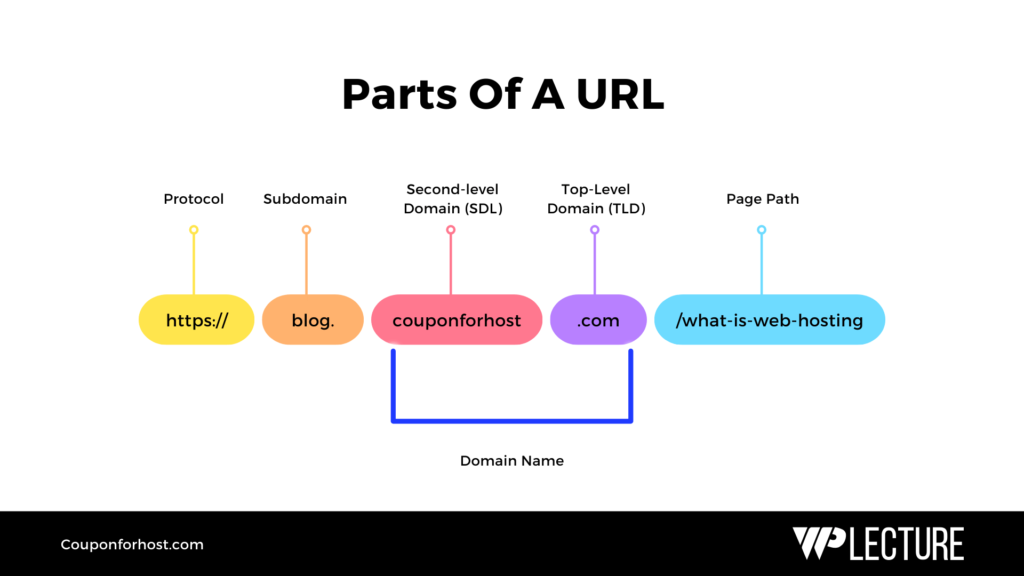
Suppose https://blog.couponforhost.com/what-is-web-hosting has a complete URL structure and is made with 5 different parts. The first part is “https://” for HyperText Transfer Protocol, which transfers data from one page to another.
Then there are three primary domains- “blog” as a subdomain prefix, “couponforhost.com” as a domain name, and “.com” showing the TLD.
Lastly, “/what-is-web-hosting” is a page address or path on that particular domain and subdomain. This URL structure helps to identify a unique address for every webpage.
HyperText Transfer Protocol
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the foundation of data communication for the web. It is used for transmitting web pages from servers to browsers.
HTTP follows a request-response model, where a client initiates an HTTP request, and a server responds. This protocol defines how messages are formatted and transmitted.
Subdomain
A subdomain functions as a distinct branch under the main domain umbrella. It allows for the categorization and hierarchical arrangement of website sections.
Using a subdomain, such as ‘store.couponforhost.com,’ can enhance organizational clarity and focus user experience on specific content.
Domain Name
A domain name serves as a memorable address for an online destination. It is unique to each website, ensuring users reach the correct site.
It is typically registered through a domain registrar, which may also host the website. From this Couponforhost.com, the Couponforhost is called the “domain” name.
TLD (Top Level Domain)
TLD stands for top-level domain, which is the last segment of a domain name. These domains are at the highest level in the hierarchical DNS.
The most common TLDs include .com, .org, and .net, indicating the nature or region of the website. They play a vital role in the structure and organization of the Internet.
Page Path
The URL’s page path indicates a page’s specific location within a website. It helps users and search engines pinpoint the exact resources needed.
Including descriptive and keyword-relevant page paths can improve a site’s SEO and user experience. Utilizing clear hierarchies in paths makes navigation more straightforward to understand.
How to Get a Domain Name?
Getting a domain name is much easier than getting a subdomain. But for this section, let’s talk about getting a domain name.
Domain name is the leading and primary address of your website. So, selecting the right domain name is crucial because it influences user perception and impacts search engine ranking.
Research some critical points before purchasing a domain name from a random web hosting company. Is the domain provider legitimate, and will it allow you to change your domain nameserver, or will it enable you to migrate your domain name to another web hosting company?
To buy a domain name, you can go with Namecheap Because is the world’s most popular and well-known web hosting company and offers a .com domain name for $5.98 for the first you.
To purchase a domain name from Name, you must go to the Namecheap.com website and then choose the domain name you want.
If the domain name is available to register, then you can add the domain name to your cart. Next, you must create an account on Namecheap.com and give them billing information.
Next, click on register at the bottom of the screen and follow the instructions to complete your purchase. Once completed, you will receive a confirmation email with all the details regarding your new domain name.
It’s essential to note that domain names must be renewed yearly, so set reminders to avoid expiration and potential loss of your domain name.
How to Get a Subdomain?
You get a subdomain for your domain name. First, you need your hosting account, But in this case, I’m using Namecheap. But you need to go to cpanel, and you can find a tab named ‘Subdomains.’
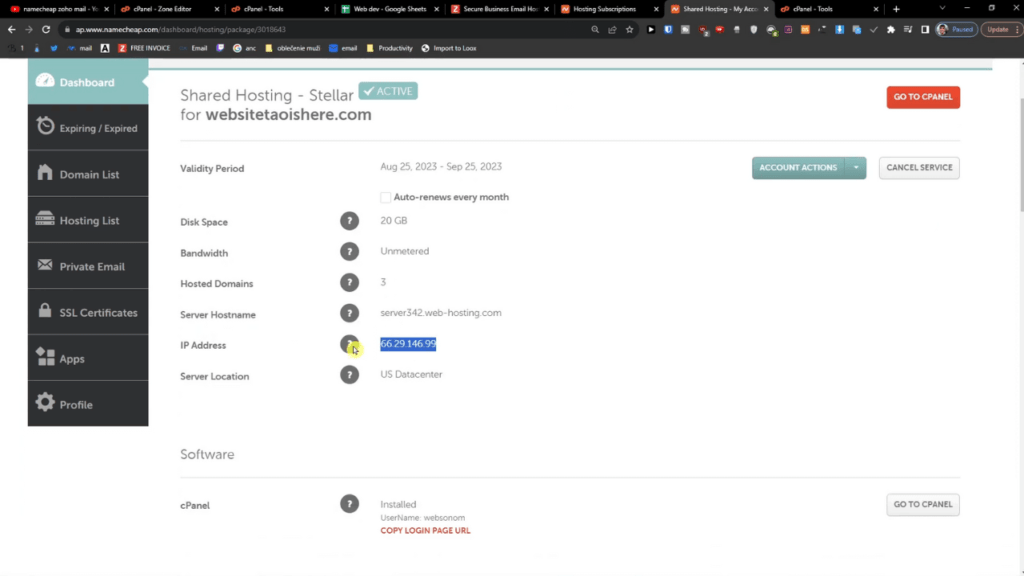
After coming to the Namecheap account, first you need to collect your IP from the Hosting List Tab, Then you need to click on the manage button of the domain where you want to create your subdomain name.
Then, go to the Advance DNS tab, click the + Add New Record button, type the Subdomain name, Select A Record from the dropdown menu, and put your IP address. Your hostname will be your subdomain.
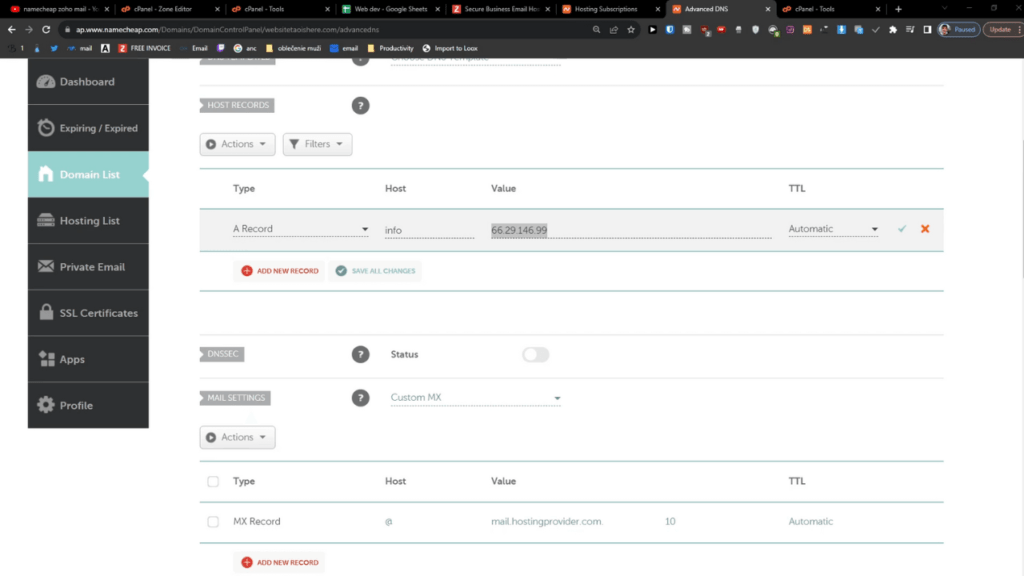
Then, click the Add New Record button and wait a few minutes. Then go to the cpanel >> Domains >> Subdomain tab if you are using Namecheap web hosting.
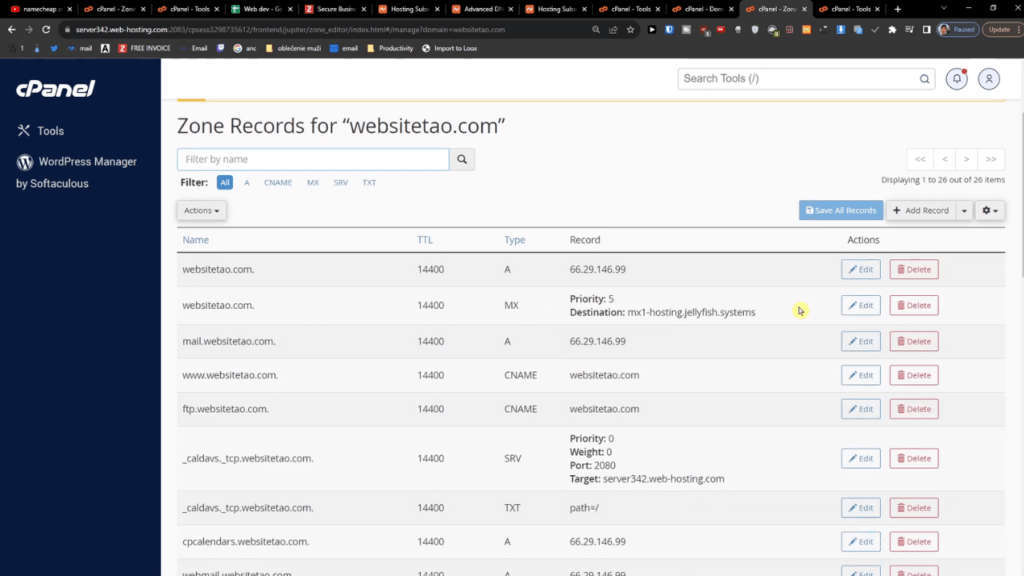
If you already registered a domain name from Namecheap.com, just log in to your account and choose ‘cPanel’ from the top menu bar. Scroll down until you find the ‘Subdomain’ tab and click on it.
In the Subdomain Maintenance area, input your desired subdomain name in the first field and select your primary domain from the dropdown menu. Then click the ‘Create’ button to generate your new subdomain.
Once created, you can manage your subdomains through cPanel or a DNS management tool. Remember that subdomains are typically used for different sections or content within the same site, whereas separate domains may be used for distinct websites.
Domain Vs Subdomain: Which Is Best For You?
Choosing between a domain and a subdomain depends on your specific online objectives. A domain indicates a primary web presence essential for brand identity.
Subdomains are best suited for organizing large websites or hosting separate areas within the same domain. They can be created quickly without additional costs.
Using a domain can contribute positively to SEO if the brand is distinct and memorable. It establishes a solid foundation for a company’s online presence.
Conversely, subdomains can dilute a brand’s search engine value but offer great flexibility to experiment with different business strategies or content areas. Consider your long-term digital strategy when deciding.
Conclusion
I hope you have enough knowledge about domain vs subdomain. Both are fundamental to your website and determine how users perceive and navigate through your online presence.
Remember, a domain name must be unique to represent your brand accurately, while subdomains provide an easy and cost-effective way to categorize and organize web content.
Whether you go with a domain or a subdomain, ensure that it adds value to your overall digital strategy and strengthens your online identity. Choose wisely and enjoy a successful web presence!
And lastly, if you need more help purchasing a domain or creating a subdomain, feel free to contact us. We are always here to help you with your online journey. Thank you!







